SMART CITY HUB RWANDA
The Smart City Hub Rwanda is a consortium under the Ministry of ICT and Innovation and partners intended to harmonize all smart city players/ partners/ implementers under one roof. The current structure of the Hub is broken down into 2 components:
Smart City “Connect” Component
This component is marketing and creating awareness around any and all smart city initiatives from the members of the consortium.
Under connect the hub is running a campaign on awareness of the dangers and proper disposal of e-waste. This campaign will target up to 2 million people through digital marketing on e-waste (what is e-waste and what isn’t e-waste)
Implementation and Innovation Component
This component is the heart of the hub’s operationalization for most of its activities around smart city solution development, strategy, and delivery of answers and outcomes to most of the problems/ challenges faced by the beneficiaries of the projects from the consortium.
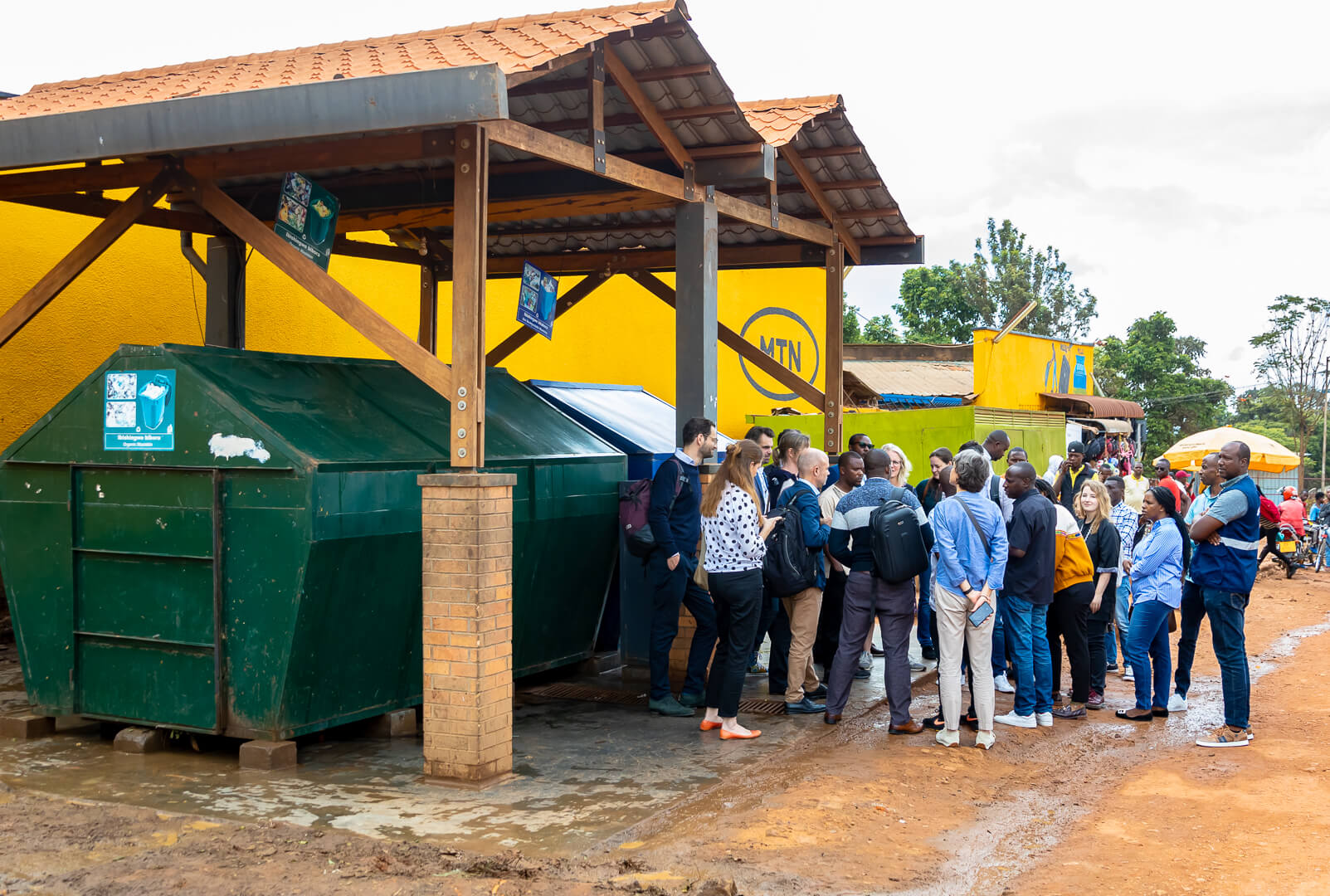
Smart waste management
The urbanization rate of the African continent has increased from 15% to 40% between 1960 and 2010 and is expected to reach 60% in 2050. The urban population in Africa will triple over the next 50 years. This unprecedented demographic boom is accompanied by an increase in challenges for governments in terms of housing, food, access to water, transport, waste management and energy supply. One of the major challenges of increased urbanization is waste management and environmental protection. Effective and sustainable waste collection and management is still a daunting exercise for the CoK that affects not only the environment but also economic and social factors such as livelihood, municipal planning and budgeting.
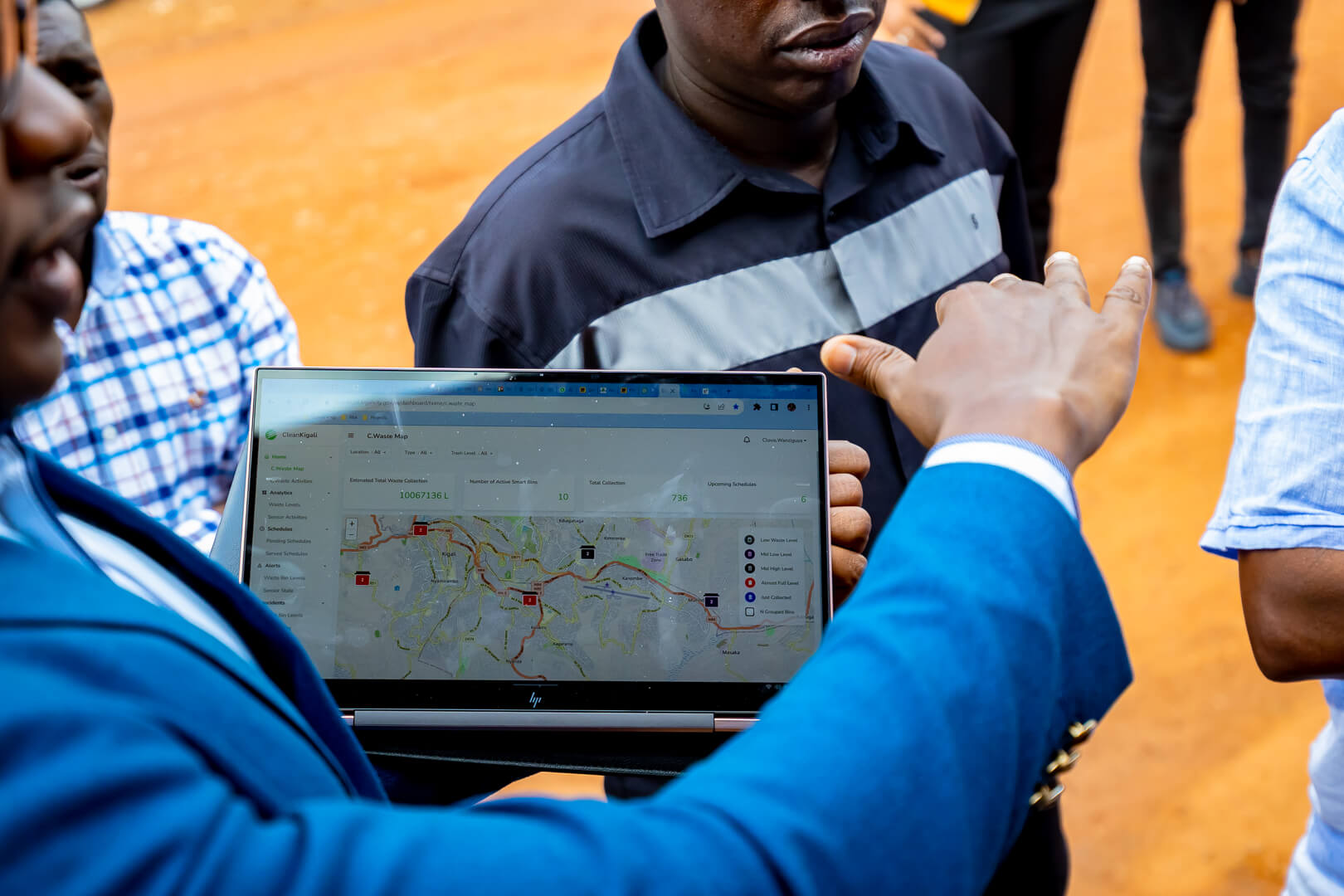

Smart waste collection and management solutions are needed to enhance regulated waste monitoring spots with fill-level sensors that provide additional information to waste management authorities as well as waste collection service providers by supporting on-demand real time waste collection.
Using locally fabricated dustbins fitted with sensors to monitor waste levels in real time, the smart waste management system aims to increase the efficiency and transparency in the process of waste collection and disposal.
Objectives:
-
Real-time data collectionData visualization for data received from the sensors.
-
Statistical reports including but not limited to waste generated, collection performance and overflows.
Impact:
-
Improved environmental sustainability.
-
Increased efficiency in collection scheduling
-
Better resource utilization
The numbers
Digital Transformation Center Rwanda has taking significant steps towards enabling digital transformation across several sectors. One of the primary objectives is to foster smart solutions that could address critical national and international challenges, such as climate change and urban mobilit
smart city startups engaged in showcasing mobility solutions.
individuals trained in smart city solutions and mobility technologies.
trategic partnerships formed in AI and smart mobility
Smart Mobility Solutions
The Smart Mobility Lab engaged both public and private sector stakeholders to address urban mobility challenges in Kigali. Through a series of workshops, collaborations, and a hackathon, innovative transportation solutions were developed that focused on sustainable urban mobility and clean energy solutions.
Founders Friday & Smart City Hub
These platforms brought together over 16 startups, entrepreneurs, and innovators to engage in dialogue about smart city solutions. The Smart City Hub facilitated discussions on urban solutions and helped promote Kigali as a growing smart city
Smart Mobility Hackthorn
The Smart Mobility Hackathon resulted in innovative solutions for Kigali’s transport infrastructure, with a focus on e-mobility and sustainable transportation systems

